

(Written by Li Min / Translated by Chen Zhiying)rom unpreparedness during the outbreak at the beginning to the emergency aid of anti-epidemic materials and personnel, and now the wide application of nucleic acid tests and the orderly inoculation of vaccines, China as well as many countries have gradually formed their own anti-epidemic mechanism and accumulated rich experience in the year fighting against the epidemic. For people from China and ASEAN countries who live closely, similar living habits and communities make the anti-epidemic experience of both sides more valuable for mutual sharing and reference.
Under the 17th China-ASEAN Expo, many valuable anti-epidemic experiences can be further exchanged and shared between China and ASEAN countries. Although these experiences can not eradicate the virus immediately, they may bring courage and hope to the people who are still in dire straits.
Making preparations for the fight against the epidemic
There is a proverb in English called “prevention is better than cure”. For the epidemic, it is obviously more important to pay attention to preventing and blocking the source of infection. At present, in many countries, basic epidemic prevention and control measures have been normalized. These measures have been integrated into people’s daily life, and even changed their living habits.
According to Salmiah Baharudin, Senior Assistant Director of the Disease Control Division of the Ministry of Health of Malaysia, Malaysian government used the app MySejahtera (which means “prosperity” in Malay) to control the epidemic. It not only can track close contacts of confirmed cases and people’s whereabouts through QR codes people showed in different locations, but also is able to locate the closest hospitals and clinics that can screen and treat patients with suspected or confirmed COVID-19. It is reported that as of August 16, 2020, 15.1 million people have registered for the app. Similar applications are also widely used in China, Singapore, Thailand, and other countries.
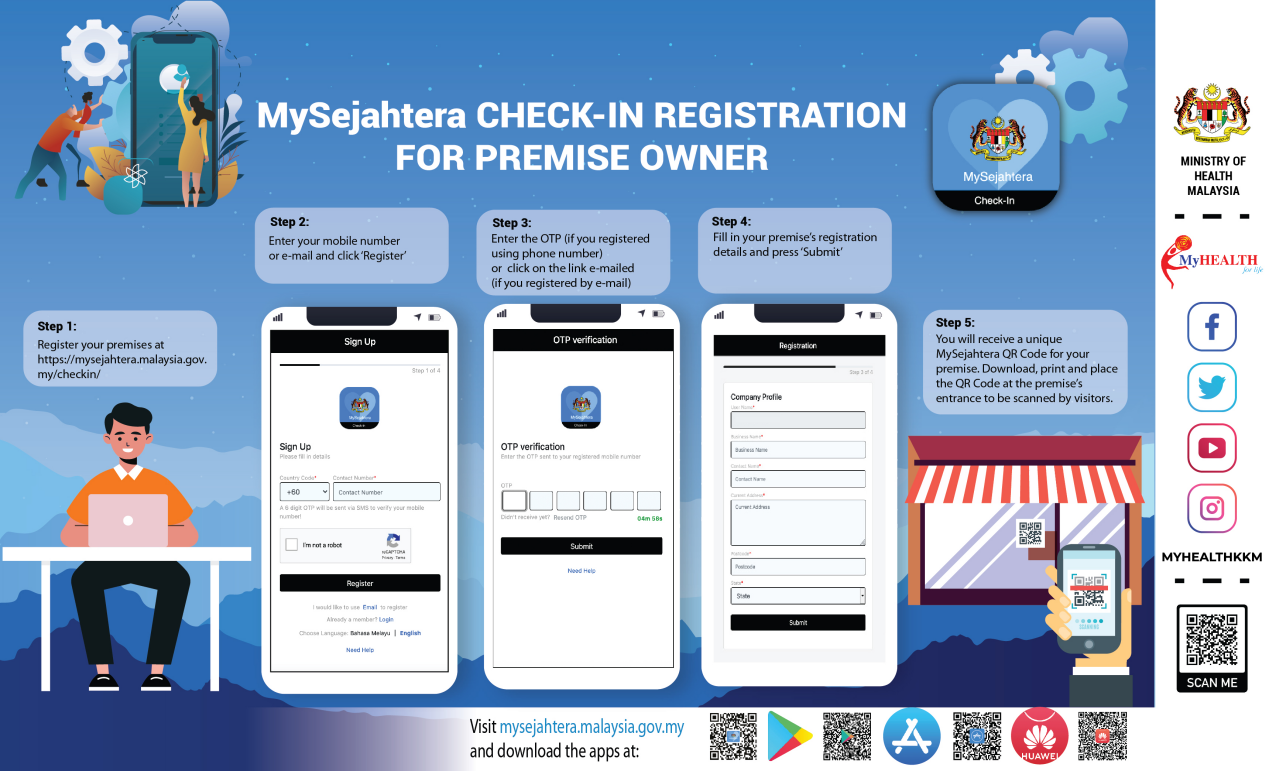
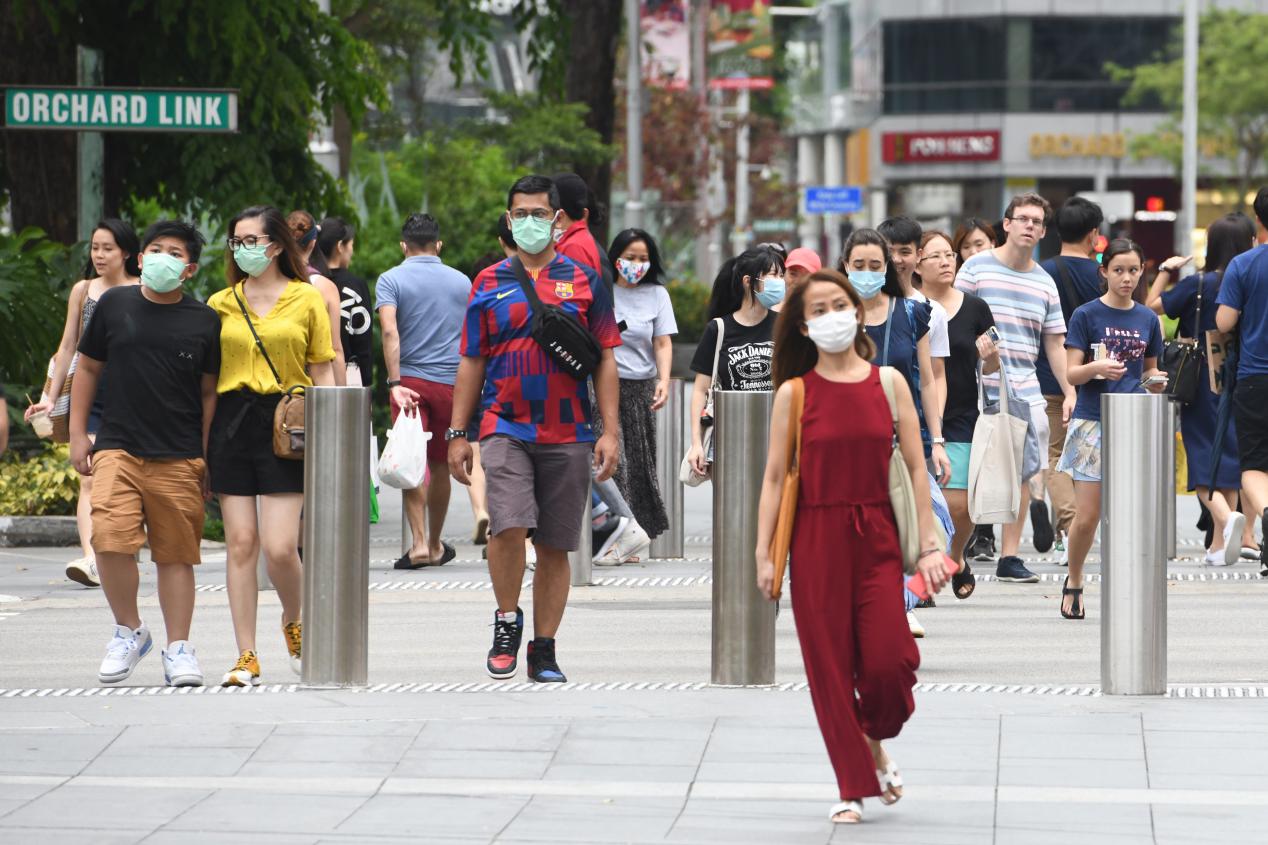
In the view of Tek Sopheap, Deputy Director of the Department of Health of Cambodia’s Bodhisattva Province, any good measure of epidemic prevention can not be separated from people’s compliance and self-discipline. “We need to let people understand the risk of the COVID-19. Also, personal hygiene, wearing masks properly, and avoiding crowd aggregation should be emphasized through mass media, social media, publicity materials, etc., since these are important measures to promote public health.
“Epidemic prevention and control is not only the responsibility of the party, the government, and the Center for Disease Control and Prevention, but also the duty of enterprises and every one of us. It requires everyone to participate in the feedback work of the epidemic and cultivate good living habits,” said Zhao Shiwen, Deputy Director of Center for Disease Control and Prevention of Yunnan Province, China.

In addition to enhancing individual awareness of epidemic prevention, countries all over the world also need to take measures to improve domestic epidemic prevention capacity, such as formulating emergency plans, strengthening the training and practice of anti-epidemic personnel, and promoting vaccination.
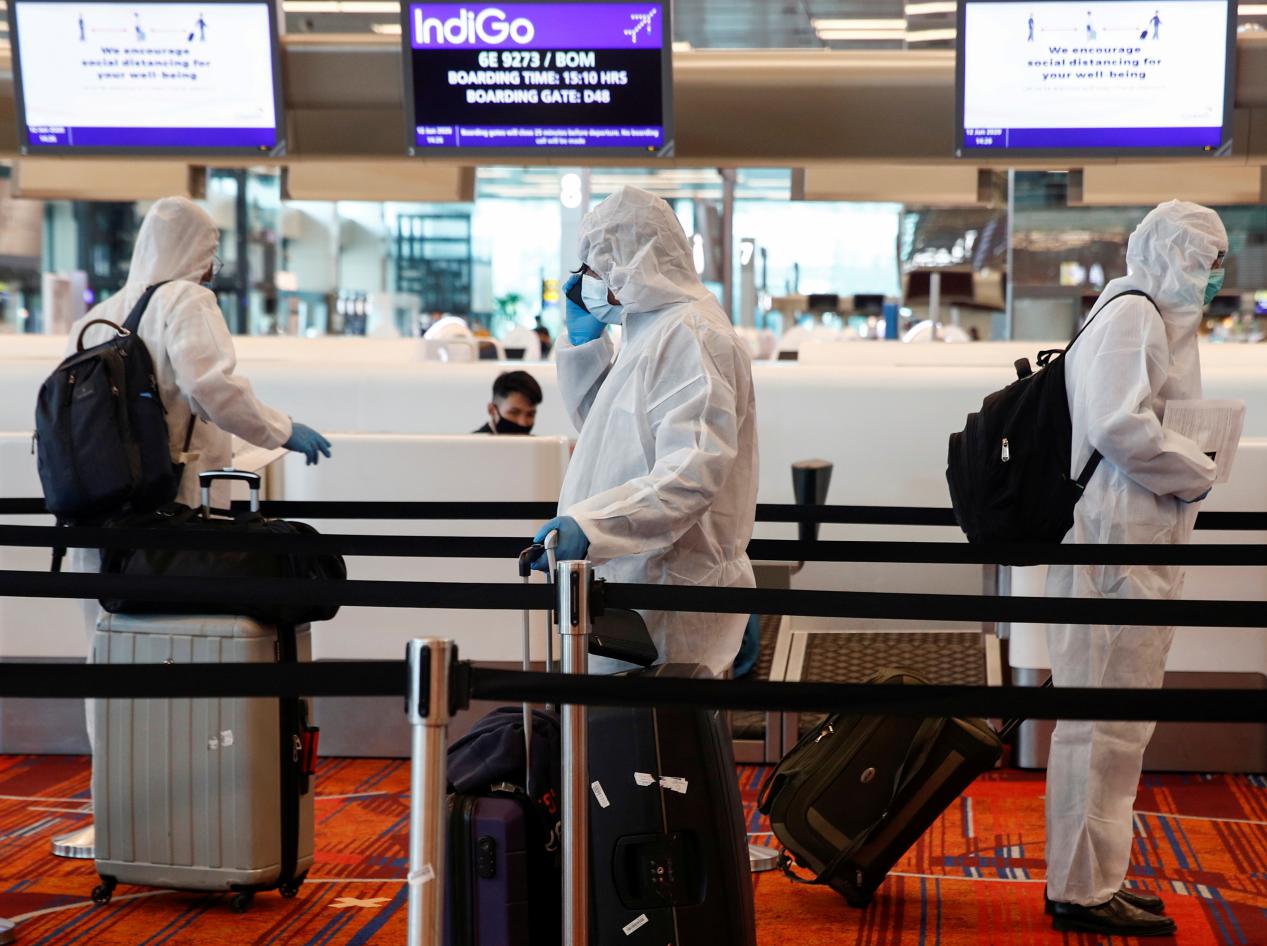
However, under the severe situation of the global epidemic, “preventing the COVID-19 from entering a region” has also become the focus of epidemic prevention and control around the globe. For entry, China and most ASEAN countries have taken measures, including but not limited to: greatly reducing international flights, submitting nucleic acid test reports, PCR and other test certificates, isolating, and receiving medical observation after entry.
“With the further discovery of the spread caused by the pollution of goods, especially frozen seafood, we have also strengthened the sampling and testing of outer packaging, containers, and transportation of imported goods, to prevent the COVID-19 from entering,” said Feng Zijian, Deputy Director of the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention.
Although many countries have strengthened the prevention and control of the epidemic at home and abroad, epidemic of different scales is still breaking out everywhere, testing the emergency response capacity of countries around the world. When the raging fire of the epidemic is ignited, how can it be quickly and accurately put out?
Three measures fighting the epidemic
“At present, there are mainly two mechanisms for the detection of epidemic. One is that clinical medical institutions timely diagnose and find the infected patients and asymptomatic-infected patients when they go to the doctor. The second is to screen high-risk groups through regular nucleic acid tests,” said Feng Zijian. And in response to sporadic outbreaks, China’s intervention measures and countermeasures mainly include search, management, nucleic acid tests, and screening.
“When the confirmed case is found, we immediately start investigating his tracks and searching other close contacts. During the epidemic, the full use of big data has continuously improved the detection probability of close contacts. Then, we will manage the community based on risk assessment, for example, block high-risk communities and carry out large-scale nucleic acid tests and screening for medium and high-risk communities. Sometimes the scope of nucleic acid tests and screening is a city, and sometimes it only targets high-risk groups and communities. This is mainly based on the judgment of the authority on the spread scope of the epidemic,” said Feng Zijian.
Although large-scale nucleic acid tests and screening in the short term is difficult to work, Feng Zijian pointed out that this can quickly find potential infected persons and block the transmission chain of the virus in time.
With the publication of confirmed cases, the physical and mental health of patients also need to be concerned. “Once a confirmed case is found out in the community. The patient and his family may be prejudiced and discriminated against. This is a social stigma, so we should protect their reputation and health,” said Tek Sopheap.
Overcoming difficulties makes us stronger
Since the discovery of the first case of the virus mutation in the UK, we know that we will still face many unknown challenges in the fight against the epidemic. However, throughout human history, the fight and confrontation between human beings and viruses have never stopped. It is through repeated challenges that human beings constantly sum up experience and upgrade their capabilities, thus making the difficulties that can not defeat us become the cornerstone for us to become stronger.
During the epidemic, serum antibody detection and whole-genome sequencing technology played a key role. According to Feng Zijian, by using these technologies, researchers can trace the transmission chain of confirmed cases and provide technical support for us to improve epidemic prevention measures.
“I think the recovery phase after the emergency response is also important. After dealing with every case, we should summarize and evaluate personnel performance, material supplement, and ability improvement,” said Zhao Shiwen. And according to his view, through practice, we can have an estimate of the consumption cycle of epidemic prevention materials, and make adequate preparations for front-line workers.

Through summary and evaluation, epidemic prevention strategies of countries around the world are also upgrading. “We will flexibly adjust the management system to ensure an effective disease prevention and control strategy in the changing situation of the epidemic,” said Sopon Iamsirithaworn, Director of the Department of Disease Control of the Ministry of Public Health of Thailand.
At present, many countries regard community participation as an important strategy of epidemic prevention management. In fact, the community has played an increasingly important role in disease prevention, outbreak, and disposal.
“Through cooperation with some Buddhist groups, we provide health education, safe funerals, celebrations, and other consulting services for the public, offer training, publicity materials, and volunteer support to the community, and standardize the management process of home isolation in the community,” said Rattanaxay Phetsouvanh, Director of the Department of Communicable Disease Control of the Ministry of Health of Laos. He also added: “Laos will continue to strengthen the positive role of communities in epidemic prevention and control by improving government services, building resilient communities, and institutionalizing community functions.”
Although anti-epidemic experiences are valuable only when they are combined with their own reality, people who have encountered greater difficulties may have such feelings: When we ask about others’ successful experiences, we not only hope to find a good way to overcome difficulties, but also hope to seek comfort and find a ray of dawn in the dark. Perhaps this is also the significance of sharing our experience in the fight against the epidemic today when the situation is still unclear.
Source: China-ASEAN Panorama
桂ICP备14000177号 Copyright@2006-2013 Guangxi China-ASEAN Panorama Magazine Agency Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved